In today’s cloud-driven world, Software as a Service (SaaS) has transformed how businesses operate, offering unparalleled flexibility and scalability. However, with this convenience comes a significant challenge: securing sensitive data against ever-evolving cyber threats. Data breaches, regulatory penalties, and loss of customer trust are just a few risks that underscore the importance of SaaS data encryption. Encryption isn’t just a technical checkbox—it’s a critical strategy for protecting data, ensuring compliance, and maintaining a competitive edge.
Introduction to SaaS Data Encryption
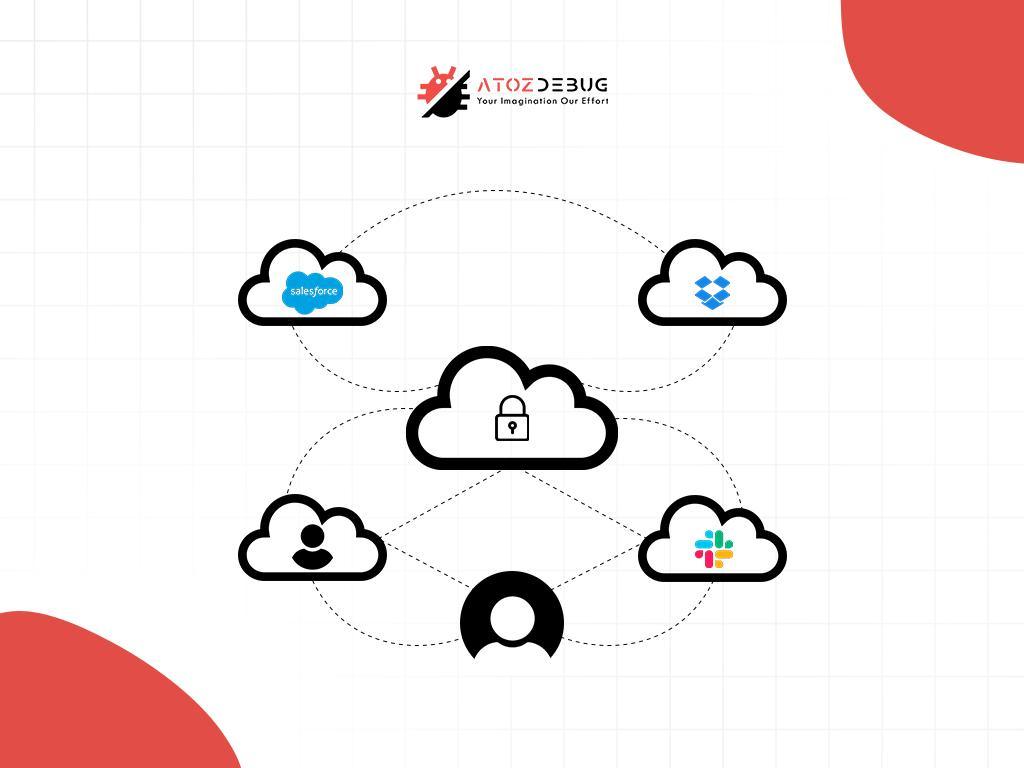
The rise of SaaS has revolutionized workflows, with platforms like Salesforce, Slack, and Dropbox powering daily operations. Yet, this reliance introduces vulnerabilities. In 2023 alone, cyberattacks targeting SaaS platforms surged, with breaches exposing millions of records. Encryption transforms this landscape by rendering stolen data useless without the decryption key, safeguarding everything from customer information to proprietary business data.
Beyond security, encryption ensures compliance with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which mandate robust data protection. For SaaS providers, offering strong encryption builds trust, while for users, it mitigates risks in a shared responsibility model.
Understanding Data Encryption
What is Data Encryption?
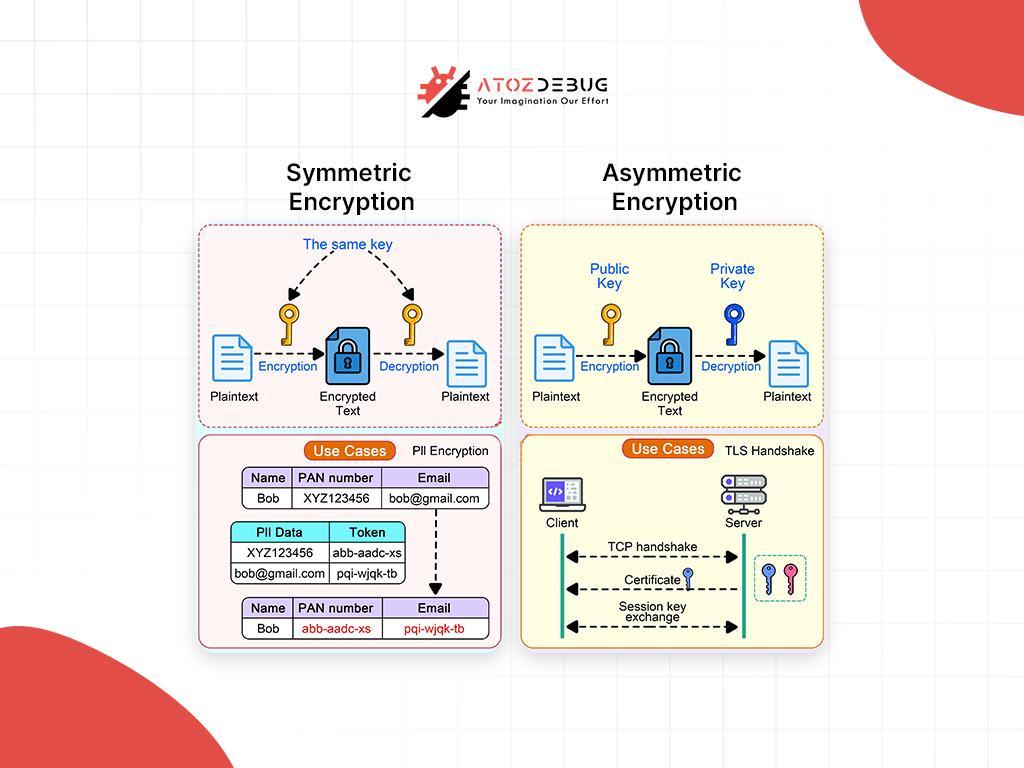
At its core, data encryption converts readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and a key. Only those with the correct key can reverse the process, ensuring confidentiality. In SaaS, encryption protects data across its lifecycle—whether stored in a database or transmitted over the internet.
How Encryption Works
Encryption relies on mathematical algorithms. There are two main types:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. It’s fast and efficient, ideal for large datasets. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), with a 256-bit key, is a widely adopted example.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Employs a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt. It’s slower but excels in secure data exchange. Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) is a common algorithm here.
The strength of encryption hinges on key length and algorithm complexity—longer keys (e.g., 256-bit) are exponentially harder to crack.
Key Management Essentials
Encryption is only as strong as its key management. Keys must be securely generated, stored, rotated, and revoked. SaaS providers increasingly offer Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) and Hold Your Own Key (HYOK) options, giving customers control over their keys. Learn more about key management from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Best Practices for Encrypting Data in SaaS
Encrypting Data at Rest
Data at rest—stored in databases, backups, or archives—must be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access if storage is compromised.
Recommended Algorithms
- AES-256: The industry standard for its speed and security.
- RSA: Useful for encrypting smaller datasets or keys.
Compliance Standards
Encryption aligns with NIST SP 800-53 guidelines and GDPR’s data protection requirements, ensuring your SaaS platform meets global benchmarks.
Encrypting Data in Transit
Data in transit—moving between users and SaaS servers—requires encryption to thwart interception.
TLS and SSL Protocols
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3: The latest protocol, offering enhanced security and performance.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): An older standard still in use but less secure than TLS.
Endpoint Authentication
Use mutual TLS (mTLS) and digital certificates to verify both sender and receiver identities, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
Tackling SaaS-Specific Challenges
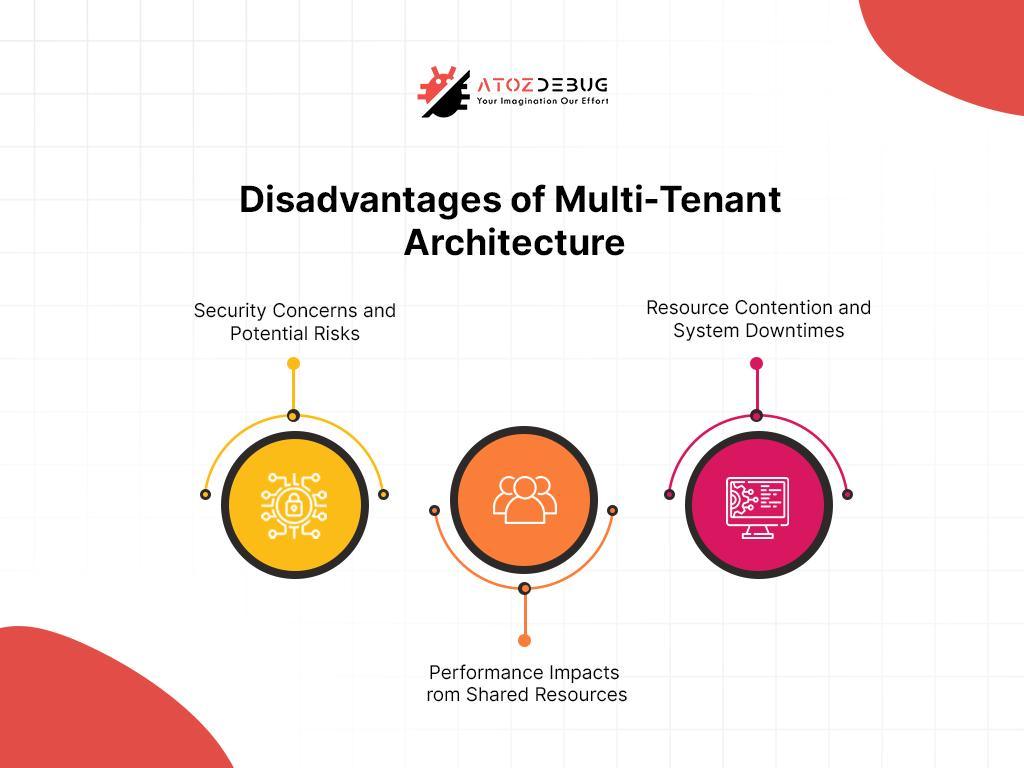
SaaS environments face unique hurdles:
- Multi-Tenancy Risks: Multiple customers share infrastructure, risking data leakage. Encryption isolates tenant data effectively.
- Shadow SaaS: Unauthorized apps used by employees can expose data. Discovery tools and encryption policies mitigate this.
Adopt a shared responsibility model, where providers secure the platform and customers encrypt their data.
Real-Time Monitoring and Incident Response
Monitor encryption in real-time with tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. An incident response plan addressing key compromise or encryption failure is vital for rapid recovery.
Balancing Security and Performance
Encryption can slow systems or raise costs. Optimize by:
- Using efficient algorithms like AES.
- Leveraging cloud-native encryption services (e.g., AWS KMS).
- Regularly benchmarking performance impacts.
Advanced Encryption Techniques
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE)
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy during processing. It’s a game-changer for SaaS applications in regulated industries like healthcare.
Benefits and Use Cases
- Enables secure third-party analytics.
- Protects sensitive data during cloud-based computations.
Though computationally intensive, FHE’s potential is vast. Explore more at IBM Research.
Quantum-Safe Encryption
Quantum computing threatens traditional algorithms like RSA. Quantum-safe encryption, using lattice-based cryptography, ensures data remains secure against future quantum attacks.
Future-Proofing
Start transitioning to algorithms like CRYSTALS-Kyber, recommended by NIST, to stay ahead.
Implementing a Zero-Trust Security Model
Zero-Trust Principles
The zero-trust model assumes no one—inside or outside the network—is inherently trustworthy. Every access request must be verified.
Encryption’s Role
Encryption underpins zero-trust by securing data end-to-end. Pair it with strong authentication (e.g., MFA) and least-privilege access controls.
Learn zero-trust strategies from the Cloud Security Alliance.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
Continuous Monitoring
Use SIEM tools and encryption health dashboards to detect anomalies, such as unauthorized key access.
Security Assessments
Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability scans quarterly to validate encryption efficacy.
Regulatory Compliance
Stay compliant with evolving laws:
- GDPR: Mandates encryption for personal data.
- CCPA: Emphasizes consumer data protection. Prepare for emerging standards like quantum-safe mandates.
Staff Training and Awareness Programs
Educating Employees
Human error causes 80% of breaches. Train staff on:
- Recognizing phishing attacks.
- Handling encryption keys securely.
Password Best Practices
Promote strong passwords and MFA to protect encrypted data access points.
Leveraging AI for Enhanced Security Management

AI-Powered Threat Detection
AI analyzes access patterns to flag threats—like unusual key usage—in real-time.
Automated Key Management
AI tools automate key rotation and auditing, reducing manual errors.
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM)
SSPM platforms monitor encryption across SaaS apps, ensuring consistency. Check out solutions from Palo Alto Networks.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Success Stories
- Salesforce: Implements BYOK and zero-trust, securing customer data across its platform.
- Dropbox: Uses AES-256 and TLS to protect files at rest and in transit.
Lessons from Breaches
The 2023 SaaS ransomware wave showed unencrypted backups are a weak link. Encrypt all data and enforce strict key controls.
Future Trends in SaaS Data Encryption
Emerging Innovations
- Decentralized Identity: Uses blockchain for secure, user-controlled encryption keys.
- AI Enhancements: Improves threat detection and key management efficiency.
Quantum-safe encryption and stricter regulations will shape the next decade.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Mastering SaaS data encryption demands a proactive, layered approach:
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit with AES-256 and TLS 1.3.
- Address multi-tenancy and shadow SaaS with tailored strategies.
- Explore advanced methods like FHE and quantum-safe encryption.
- Adopt zero-trust, leverage AI, and conduct regular audits.
- Train staff and stay compliant with evolving standards.
In a world of escalating cyber threats, robust encryption isn’t optional—it’s your competitive advantage.Start strengthening your SaaS security today. Dive deeper with resources from NIST and Cloud Security Alliance.