For Software as a Service (SaaS) providers, uninterrupted service isn’t just a priority—it’s a necessity. A single outage can cost thousands per minute, damage your reputation, and drive customers to competitors. According to a 2024 Gartner report, cloud disruptions average $5,600 per minute in losses, with poor recovery strategies significantly increasing customer churn.
This guide provides an actionable roadmap to building a robust disaster recovery (DR) strategy for your SaaS business. From understanding core DR concepts to implementing cutting-edge recovery solutions, this blog will help you safeguard your platform against disruptions.
Why Disaster Recovery for SaaS Matters
The High Stakes of Availability
SaaS platforms operate 24/7, and downtime can lead to massive financial and reputational losses. While high availability (HA) solutions aim to prevent downtime, disaster recovery ensures rapid restoration when the unexpected happens—whether it’s a cyberattack, provider outage, or human error.
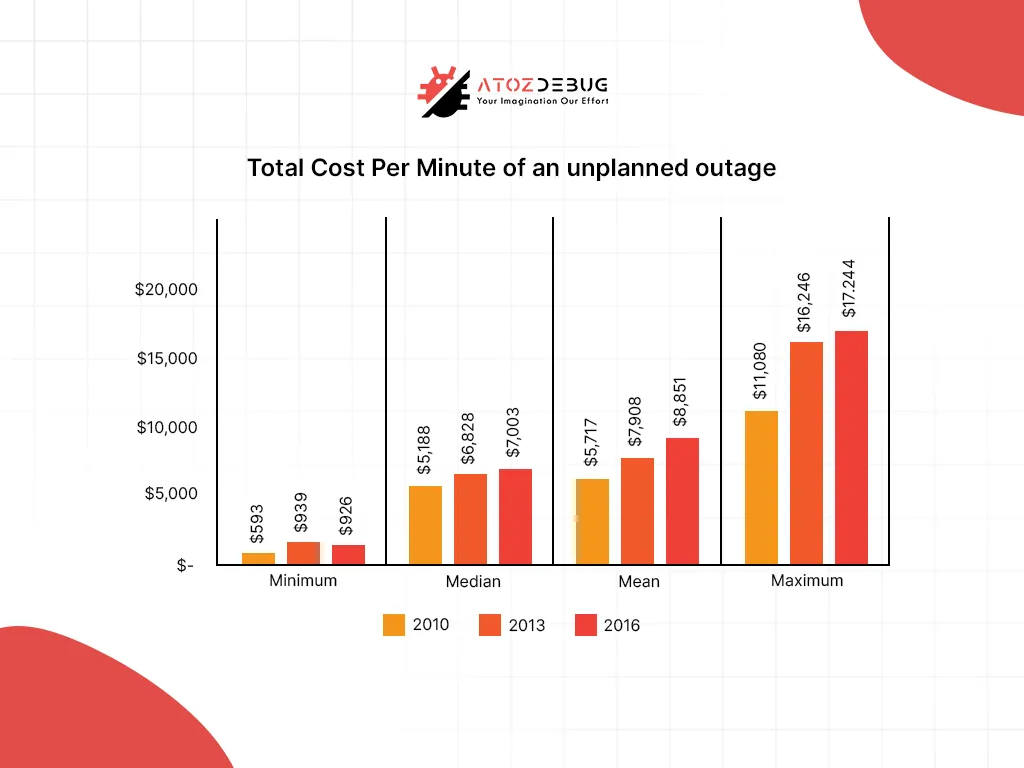
The Cost of Being Unprepared
Failing to plan for disasters can have severe consequences:
- Revenue Loss: Downtime directly affects your bottom line, especially for mission-critical SaaS platforms.
- Customer Churn: A 2023 survey found that 62% of SaaS users would switch providers after experiencing two outages.
- Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with data protection laws can lead to hefty fines.
Basics Disaster Recovery for SaaS
Defining Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery in SaaS focuses on restoring application functionality and data integrity after an outage. Unlike high availability, which minimizes downtime, DR ensures a structured recovery when failures occur.
Key Recovery Metrics
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): Maximum allowable downtime before recovery.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Maximum data loss acceptable, measured in time.
- Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD): Longest outage duration a business can withstand before serious consequences.
Understanding SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS DR Responsibilities
| Cloud Model | Who’s Responsible for DR? | What You Should Focus On |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Your provider takes care of most things | Make sure you back up your customer data, keep an eye on uptime promises (SLAs), and have a plan for handling service disruptions. |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | It’s shared—you and your provider both play a part | You’re in charge of app-level backups and testing your recovery steps, while your provider handles the underlying infrastructure. |
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | You’re fully responsible | You’ll need to manage everything—from storing backups and setting up failovers to defining RTO/RPO goals and testing your plan regularly. |
- SaaS: Your provider manages DR, but you must secure customer data.
- PaaS: You handle application recovery within the provider’s infrastructure.
- IaaS: You are responsible for full-stack recovery, requiring a broader DR strategy.
Assessing Risks and Business Impact
Common SaaS Threats
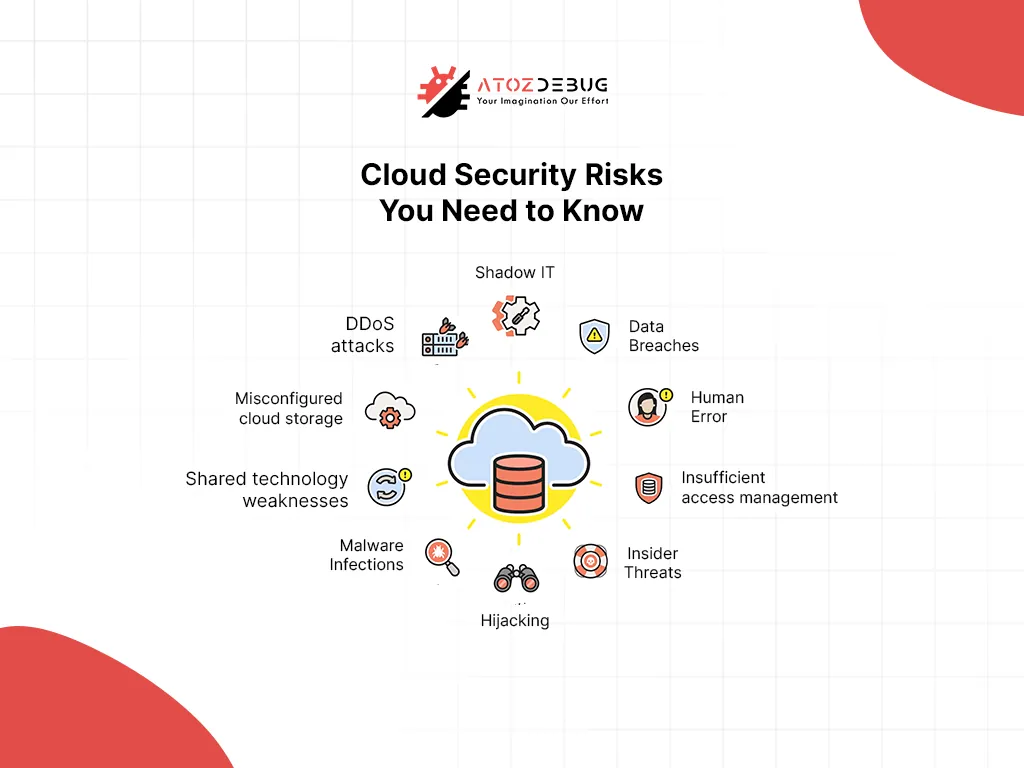
SaaS platforms are vulnerable to multiple risks, including:
- Cyber Threats: Ransomware, DDoS attacks, and data breaches.
- Cloud Provider Downtime: Even major providers like AWS and Azure experience outages.
- Human Errors: Accidental data deletions or faulty updates.
Conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
To identify vulnerabilities and recovery priorities:
- Rank Critical Services: Prioritize mission-critical functions like payment processing.
- Trace Dependencies: Identify service interdependencies to avoid recovery blind spots.
Crafting a SaaS Disaster Recovery Plan
Essential Components
A strong DR plan includes:
- Incident Response Playbooks: Clear steps for handling different disaster scenarios.
- Backup and Restore Strategies: Well-defined processes for quick data recovery.
- Failover Mechanisms: Instant switchover to backup systems during outages.
Cloud-Native Disaster Recovery Options
- Active-Active Setup: Multiple live systems split the load, ensuring seamless failover.
- Active-Passive Setup: A backup system remains on standby, activated during failures.
Implementing a Technical Disaster Recovery Strategy
Setting RTO and RPO Targets
Define tiered recovery goals based on application priority:
- Critical Apps: RTO < 10 seconds, RPO < 1 minute.
- Key Apps: RTO < 5 minutes, RPO < 15 minutes.
- Non-Critical Apps: RTO < 1 hour, RPO < 1 hour.
Backup and Redundancy Strategies
- Immutable Backups: Protect against ransomware attacks.
- Geo-Redundant Storage: Store backups across multiple locations to prevent regional failures.
- Multi-AZ and Multi-Region Deployments: Distribute resources across zones and regions for resilience.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid DR Strategies
Avoid vendor lock-in by diversifying cloud providers (e.g., AWS + Azure) or blending cloud and on-prem infrastructure.
Automation for Faster Recovery
- DNS Failover: Automatically reroutes traffic to healthy servers.
- Kubernetes Failover: Enables seamless workload shifting between clusters.
- Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Replication: Choose between real-time mirroring (zero data loss) or cost-effective near real-time replication.
Managing Vendor SLAs and Compliance
Choosing a Cloud Provider with Strong DR Capabilities
- 99.99%+ Uptime Guarantees: Ensure high availability commitments.
- SLA Penalties: Compensation for downtime-related losses.
- Data Portability: Secure easy migration options.
Compliance Considerations
Ensure compliance with industry regulations:
- HIPAA (Healthcare SaaS): Protects patient data.
- PCI DSS (Payment SaaS): Safeguards cardholder data.
- SOC 2 Type II & ISO 27001 Certifications: Indicate strong security and DR measures.
Testing and Validating Your Disaster Recovery Plan
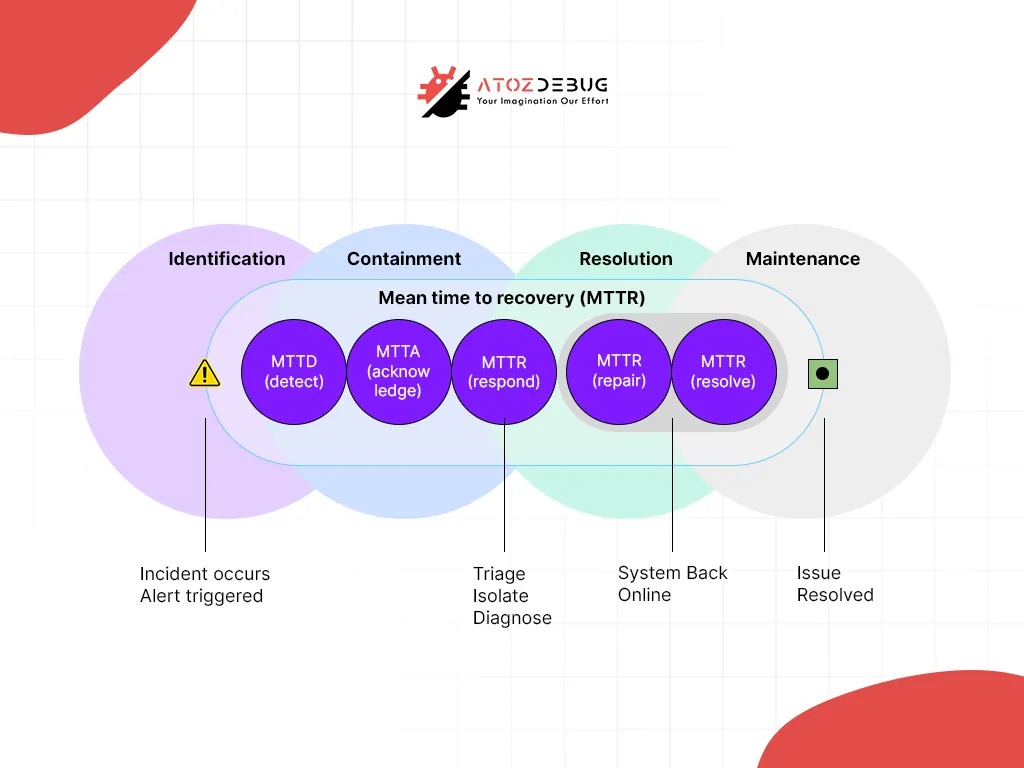
Testing Methods
- Tabletop Exercises: Simulate disaster scenarios to refine responses.
- Full Failover Drills: Conduct live tests to assess system resilience.
Measuring Success
- Consistency Score: Evaluates recovery reliability.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Tracks restoration speed.
Handling Incidents and Communication
Stakeholder Communication
- Customer Alerts: Pre-drafted notifications for transparency.
- Regulatory Reporting: Ensure timely compliance with reporting obligations.
Incident Response Workflow
- War Room Activation: Assemble a crisis management team.
- Decision Escalation: Define roles for key decision-makers.
Future Trends in SaaS Disaster Recovery
AI-Powered Prediction and Prevention
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is enhancing DR by detecting anomalies before they cause failures.
Chaos Engineering for Stress Testing
Companies like Netflix use controlled failure simulations to identify weaknesses and improve resilience.
Emerging Technologies
- Quantum-Proof Security: Future-proofing encryption against quantum computing threats.
- Edge Computing for Faster Recovery: Reducing latency by processing data closer to the source.
Final Thoughts: Your SaaS DR Action Plan
Disaster recovery is a continuous process that evolves with emerging threats and technologies. Here’s a quick roadmap to getting started:
- Identify Risks: Assess vulnerabilities and mission-critical services.
- Set RTO and RPO: Define recovery objectives based on business needs.
- Implement Backup Strategies: Choose geo-redundancy and immutable storage.
- Deploy Failover Mechanisms: Utilize multi-cloud or hybrid setups for resilience.
- Test and Optimize: Regularly run simulations and update your plan based on findings.
By proactively investing in a solid disaster recovery strategy, SaaS providers like Us (AtoZDebug) can ensure service continuity, maintain customer trust, and minimize financial losses. Start strengthening your DR plan today to stay ahead of potential disruptions.
FAQs
Q1. What’s the difference between High Availability and Disaster Recovery?
High availability keeps systems running to prevent downtime. Disaster recovery focuses on restoring systems after a disruption occurs.
Q2. How often should you test your SaaS DR plan?
Ideally every quarter—or at least twice a year—with both tabletop and live failover drills.
Q3. Do SaaS companies need DR if the provider manages infrastructure?
Yes. While providers manage hardware, SaaS companies are responsible for data recovery, customer access, and incident communication.
Q4. What DR tools are best for SaaS?
Look for tools that support Kubernetes failover, immutable backup, and multi-cloud readiness (e.g. Zerto, Cohesity, SpinBackup).
Also Read:
Mastering SaaS Problem Statements
Trending SaaS Business Ideas That Can Generate the Most Revenue