As businesses continue to grow, using technologies is key to staying ahead. Over the years, cloud computing has become a game-changer in this regard. It offers companies the flexibility and growth potential needed to improve their operations.
Moving to the cloud allows them to focus only on their core strengths while leaving the complicated tasks of managing infrastructure to experts. Broadly there are three cloud services models, such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, with each offering different levels of control, customization, and management based on the needs of the business.
But, people often get confused about understanding the differences between them. In this article, we’ll explain these cloud-based models in simple terms. At the end of this guide, you’ll surely be able to decide which one is right for your business.
What Are Cloud Service Models and Why They Matter
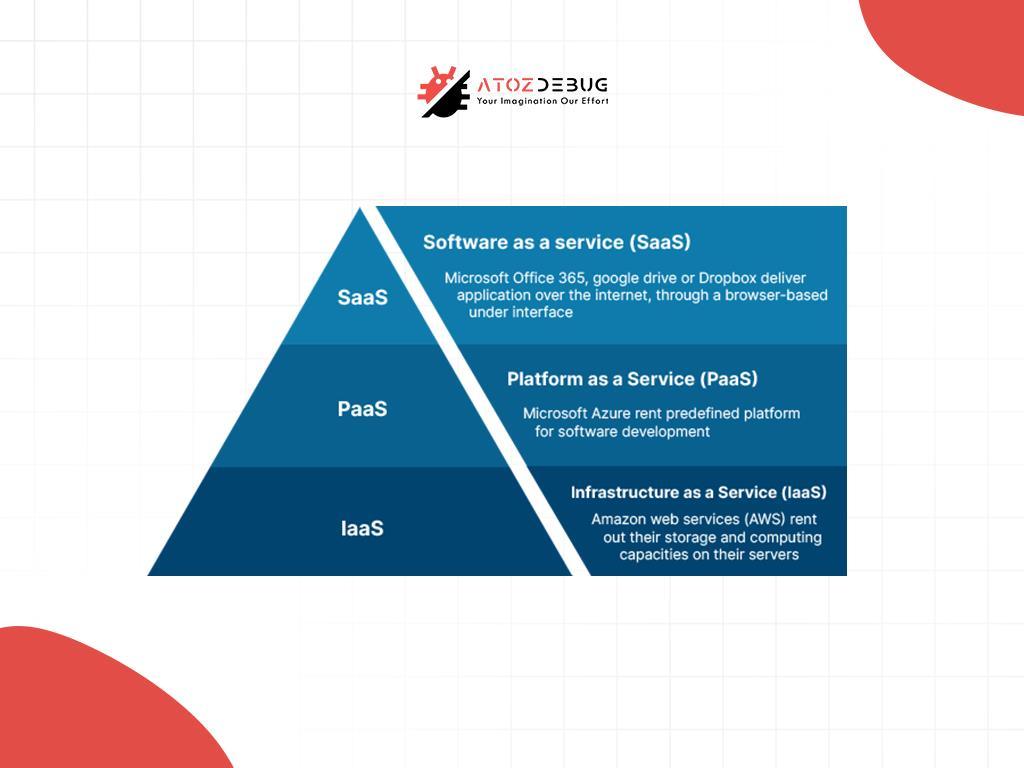
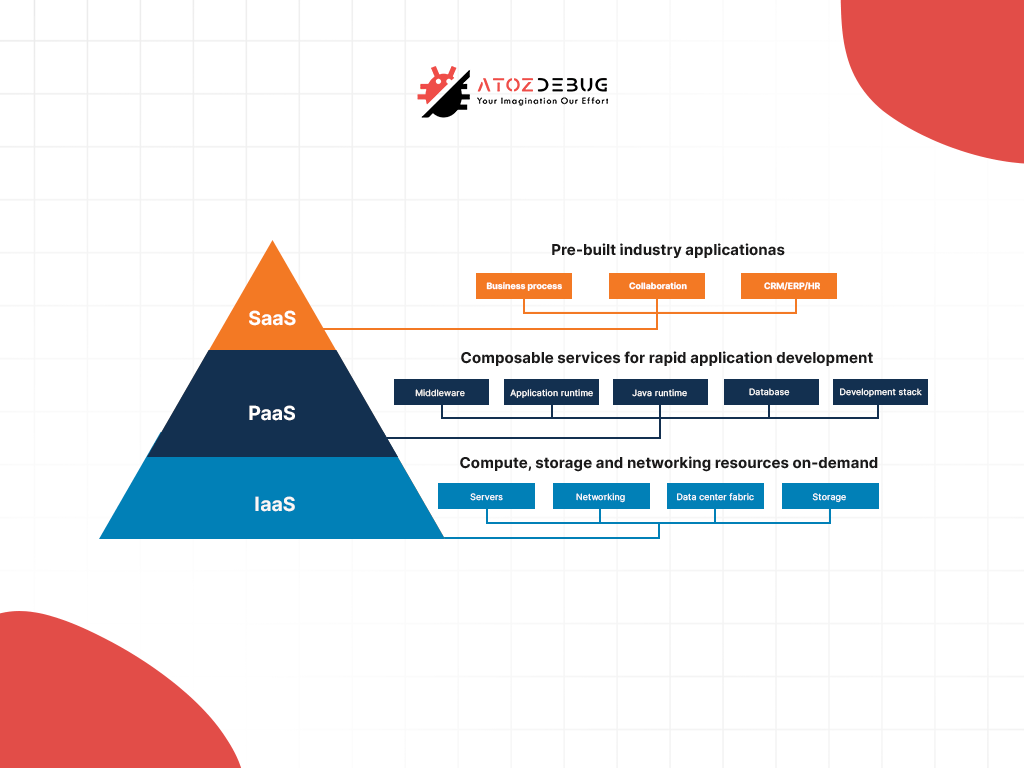
Cloud service models are fundamental components of cloud computing architecture. They allow businesses and individuals to use cloud computing based on their unique needs. These models are categorized into three primary types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Each cloud service model offers distinct advantages. IaaS provides scalable virtual resources like servers, storage, and networking, which enables organizations to manage their infrastructure without investing in costly on-premises hardware.
PaaS simplifies application development by offering pre-built frameworks, operating systems, and tools, allowing developers to focus on coding rather than infrastructure. SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance. This makes it ideal for businesses looking for quick deployment and scalability.
Why Cloud Service Models Matter?
The importance of cloud service models lies in their flexibility and efficiency. By utilizing these three models, companies can literally work more efficiently, enhance collaboration, and ensure faster launch of products in the market.
At the same time, they can enjoy the security and reliability that cloud computing architecture offers. For example, startups can use SaaS for rapid growth, while enterprises may rely on IaaS to handle complex workloads.
Exploring SaaS PaaS and IaaS Cloud Infrastructure
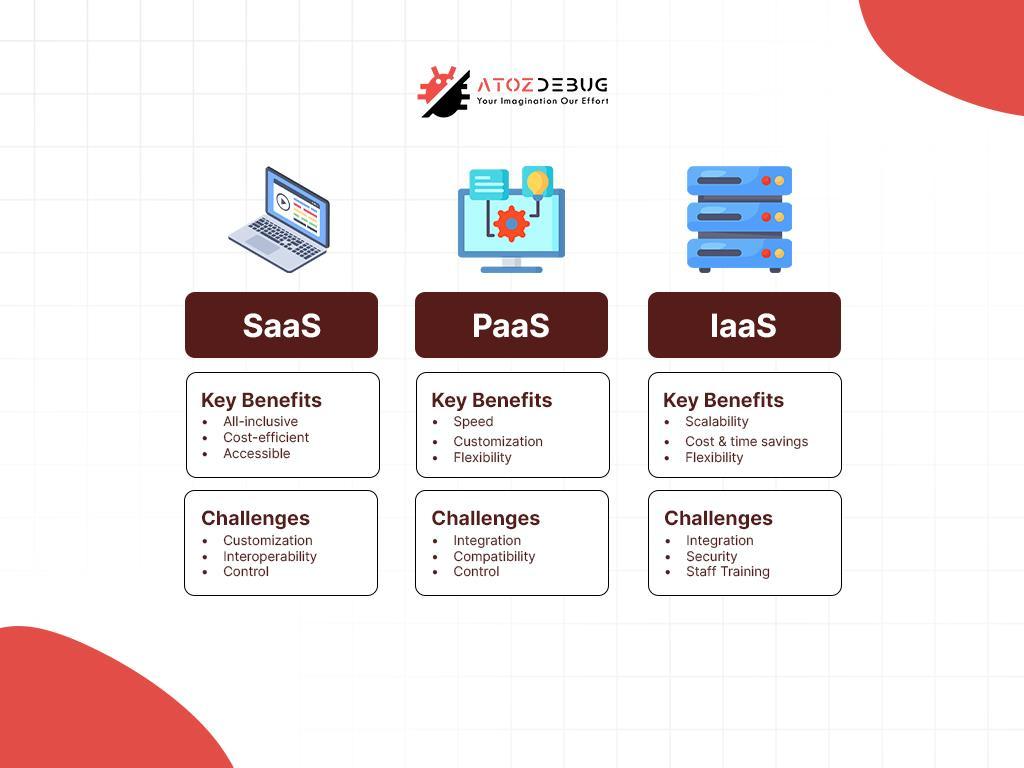
Cloud infrastructure provides businesses with scalable and flexible solutions, offering three main service models to meet different needs. These models make it simpler for businesses to use technology in the best way for their goals. There are three primary cloud service models:
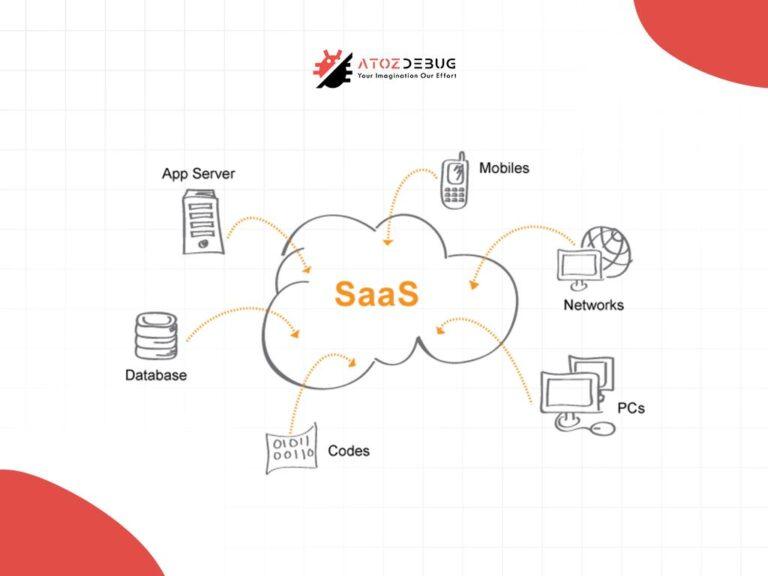
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Use Case: SaaS is perfect for businesses that require ready-to-use applications without managing underlying infrastructure. Popular examples include CRM tools like Salesforce.
Key Feature: SaaS takes care of installation, maintenance, and updates, which makes it cost-effective and easy to use from anywhere with an internet connection. It’s great for remote work, but customization is often limited, and changing vendors can be difficult.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Use Case: PaaS meets developers by providing a platform for building, testing, and deploying applications without worrying about infrastructure management. Examples of Platform as a Service include Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine.
Key Feature: PaaS boosts development speed, encourages team collaboration, and minimizes infrastructure costs. However, businesses rely heavily on the provider, which might limit control and interoperability between platforms.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Use Case: IaaS is designed for companies needing complete control over their IT environment, such as hosting custom applications. Examples of Infrastructure as a Service include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
Key Feature: IaaS offers exceptional scalability and flexibility, adapting to resource needs dynamically. However, it demands skilled personnel to manage the infrastructure effectively, which makes it complex for smaller teams.
How Cloud Providers Shape the Cloud Computing Ecosystem
Cloud providers always play a key role in cloud computing. They help businesses access powerful computing resources through services like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Major cloud providers such as Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud lead the market by offering a variety of services to meet different business requirements.
For example,
– IaaS providers, offer scalable IT infrastructure components like storage, compute power, and networks. This helps businesses save on the costs and complexity of managing their own physical data centers.
– PaaS providers take it a step further, providing the tools and platforms necessary for developing and deploying applications without having to manage underlying hardware.
– SaaS providers, on the other hand, deliver ready-to-use applications, handling everything from infrastructure to updates, which allows businesses to access software on-demand.
These cloud models collectively contribute to the growth of the cloud computing ecosystem by enabling businesses to scale, innovate, and enhance productivity without heavy investments in on-premise infrastructure. Cloud providers create a flexible environment where businesses can choose services from different providers to fit their needs. This flexibility is important because it lets companies tailor their cloud strategy and use resources more efficiently.
As cloud computing keeps evolving, providers are exploring new technologies like machine learning, edge computing, and containerization. These innovations are helping the cloud computing ecosystem grow and improve even more.
Unveiling Cloud Cost Models and Deployment Strategies
Cloud cost models and deployment strategies are crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their cloud resources effectively. Knowing these components well, organizations can customize their cloud computing experience to meet both performance goals and budget constraints.
Cloud Cost Models
The right cloud cost model ensures that businesses only pay for what they use. This enhances cost efficiency. Popular cloud cost models include:
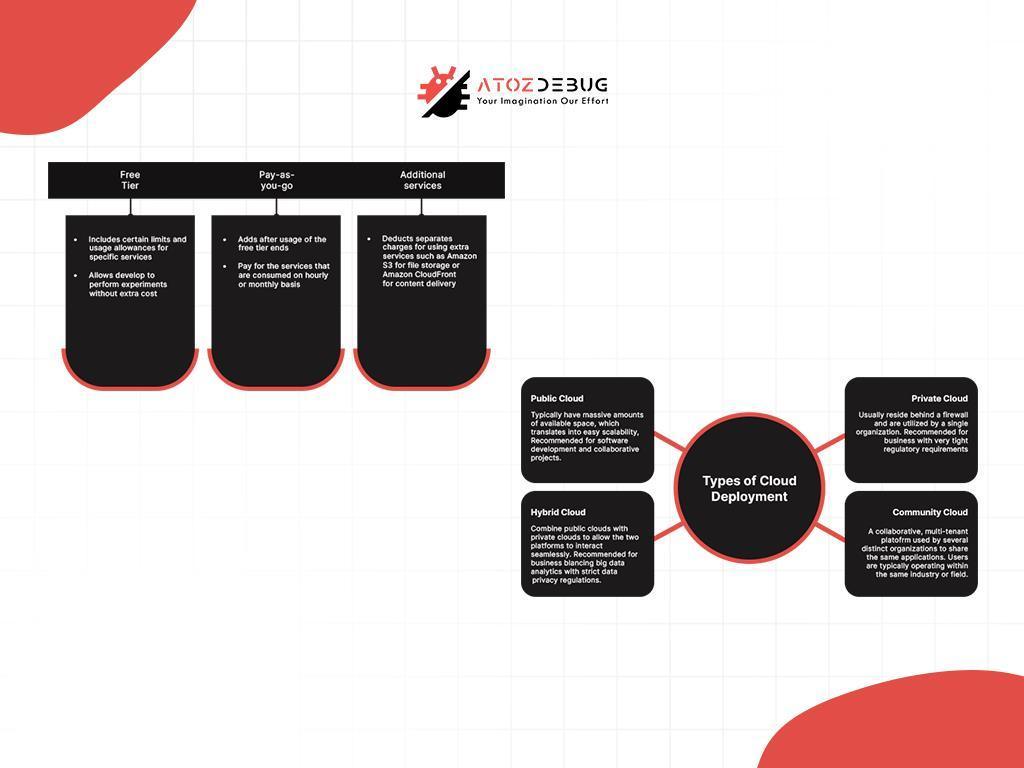
- Pay-As-You-Go: This model, offered by providers like AWS and Google Cloud, charges businesses based on the actual usage of resources. It is perfect for companies with variable workloads or those just starting with cloud adoption.
- Reserved Instances: Businesses can save money and plan costs better by signing long-term contracts, which often come with discounted rates.
- Savings Plans: AWS and Google Cloud have flexible savings plans that offer discounts based on how much you commit to using. This helps businesses save more as their cloud usage increases.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Picking the right cloud computing deployment model is key to ensuring scalability and security. The main types of deployment models are:
- Public Cloud: Hosted by third-party providers like Google Cloud and AWS, the public cloud offers shared resources with easy scalability and lower costs. This is ideal for businesses looking for quick growth without managing infrastructure.
- Private Cloud: This model gives businesses their own dedicated resources, offering better control and security. It’s often chosen by industries that deal with sensitive data.
- Hybrid Cloud: The hybrid cloud mixes public and private clouds, letting businesses keep important data on a private cloud while using the public cloud for less-sensitive tasks. This setup offers flexibility and scalability.
In short, the best cloud strategies combine the right cost plans with the right deployment options. This helps businesses save money while improving security and scalability.
Whether using the affordable public cloud or the hybrid cloud’s mix of security and scalability, picking the right approach is key to long-term success in the cloud.
Overcoming Challenges in Cloud Environments
Working in the cloud environment indeed has many benefits, but it also comes with challenges. To succeed, it’s important to understand these challenges and take action to address them.
1. Managing Multicloud and Hybrid Cloud Setups
Organizations often use different cloud platforms to meet various needs, which can make things more complex. The challenge is managing everything smoothly across these different platforms.
Solution: To solve this, businesses can use centralized management tools. These tools help simplify processes, improve visibility, and manage resources better across different platforms. This approach helps reduce inefficiency and keeps things running smoothly in multicloud and hybrid cloud environments.
2. Optimizing Cloud-Native Applications
Cloud-native applications are designed to take full advantage of the cloud’s scalability, but managing their performance can be challenging, especially as workloads grow.
Solution: Container orchestration tools, such as Kubernetes, help automate the deployment, scaling, and management of these applications. By using such tools, businesses can ensure seamless functioning while minimizing manual intervention and optimizing resource usage.
3. Strengthening Security and Governance
With data stored and transmitted across cloud environments, ensuring security is crucial. Breaches or compliance failures can result in significant risks.
Solution: To keep things secure, businesses need to use strong measures like encryption, access controls, and regular security checks. It’s also important to follow industry rules to protect sensitive data and maintain trust.
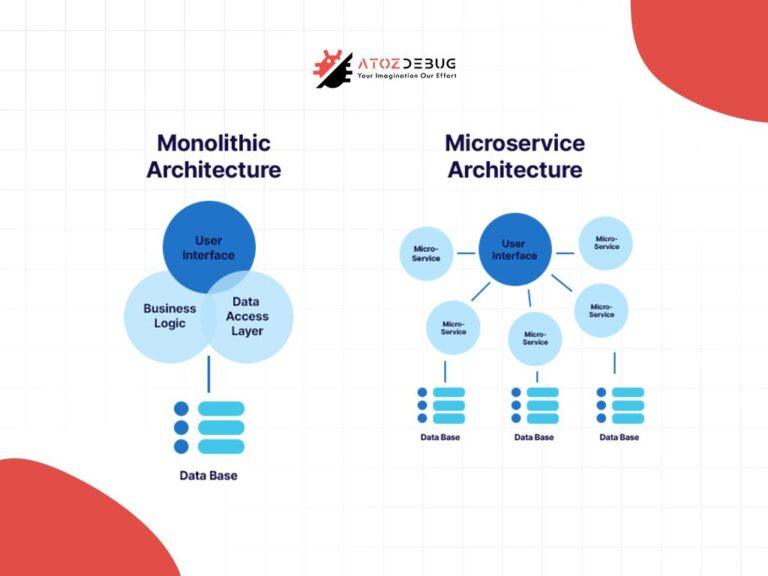
4. Adapting to Microservices Architecture
The transition to microservices can introduce challenges in communication and monitoring between services.
Solution: Using tools like service meshes helps manage the connections between microservices, making communication easier, secure, and efficient as services grow.
5. Managing Performance and Cost Optimization
Cloud services can scale easily, but managing performance and costs can be tricky, especially when workloads change. If not monitored properly, costs can quickly rise.
Solution: Implementing automated cost management tools and performance monitoring solutions ensures that organizations can adjust resources dynamically. These tools help prevent unnecessary expenses while optimizing performance to meet the demands of the business.
By using the right tools and strategies, organizations can fully take advantage of their cloud environments, reduce risks, and improve performance.
Conclusion
At last, cloud computing has revolutionized business operations. It provides smart ways to manage virtual machines, virtual storage, and data storage.
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS play a big role in this change. Each has different characteristics and meets different needs. Whether it’s making software reliable, helping build apps smoothly, or managing networking and analytics, these models let companies grow and adapt easily.
To choose the right cloud service model, you need to think about your goals, technical skills, and budget. The right choice can boost efficiency, cut costs, and set your business up for long-term success in the current fast-moving digital world.
Interested in knowing more? If so, contact us for personalized advice on selecting the best cloud model for your business. You can also download our comprehensive guide to learn how cloud services can help your business thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is SaaS, and when should a business use it?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It’s best for businesses that want to use ready-made applications like email, CRM, or accounting tools without worrying about installation or maintenance.
2. How is PaaS different from traditional software development?
PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers a complete environment for developers to build and deploy applications online. Unlike traditional development, you don’t need to manage servers or infrastructure—it’s all handled by the provider.
3. Why do some companies prefer IaaS over SaaS or PaaS?
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) gives businesses full control over their IT resources. Companies that need custom setups or want to run their own software often prefer IaaS because it’s flexible and scalable.
4. Can a company use SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS at the same time?
Yes, many companies use a mix of all three depending on their needs. For example, they might use SaaS for email, PaaS for app development, and IaaS for hosting their website or storing data.
5. Is it expensive to move to cloud services like SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS?
It depends on what you need. SaaS can be affordable for small businesses, while IaaS might cost more but offers greater control. Most cloud services use a pay-as-you-go model, so you only pay for what you use.